RESEARCH
Key ongoing initiatives
THERAPEUTIC FOCUS AREAS
Type 2 Diabetes Studies
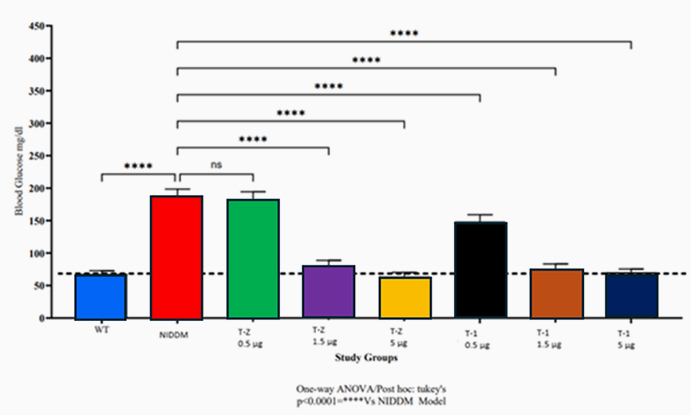
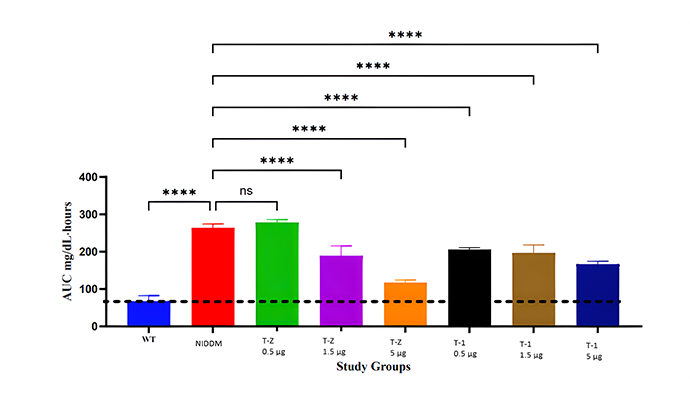
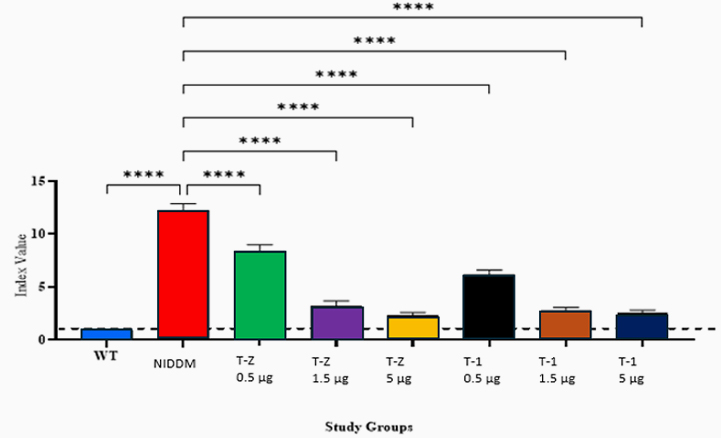
Building on zebrafish success, Telomir is testing a rat diabetic model to confirm Telomir-1’s efficacy in reversing metabolic parameters, including reduced insulin resistance (HOMA-IR).
PROGERIA RESEARCH
Following promising C. elegans results, Telomir-1 restored lifespan and normalized aging in wrn-1 mutant nematodes (a model for Werner Syndrome), with microfluidics revealing enhanced longevity and physiology.
aLZHEIMER’S DISEASE & OTHER NEURO – DEGENERATIVE DISEASES
Investigating Telomir-1 for its potential to mitigate cognitive decline and neurodegeneration associated with Alzheimer’s and Fredrick’s Ataxia.
MACULAR DEGENERATION (AMD)
Exploring Telomir-1’s role in addressing retinal cell degeneration and Drusen formation, which occurs when metals like copper or iron accumulate to harmful levels
wilson’s disease study
Investigating Telomir-1’s effects on copper regulation in preclinical models.
cancer models
Exploring anti-cancer applications using xenograft studies.
virus
Exploring Telomir-1 effects on viral infections.
pre-clinical research
pre-clinical research
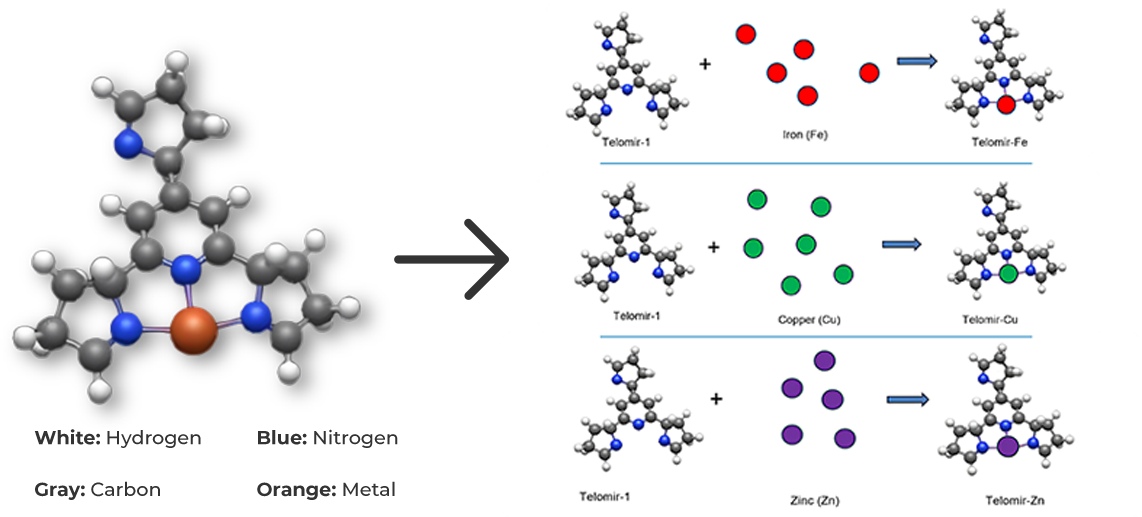
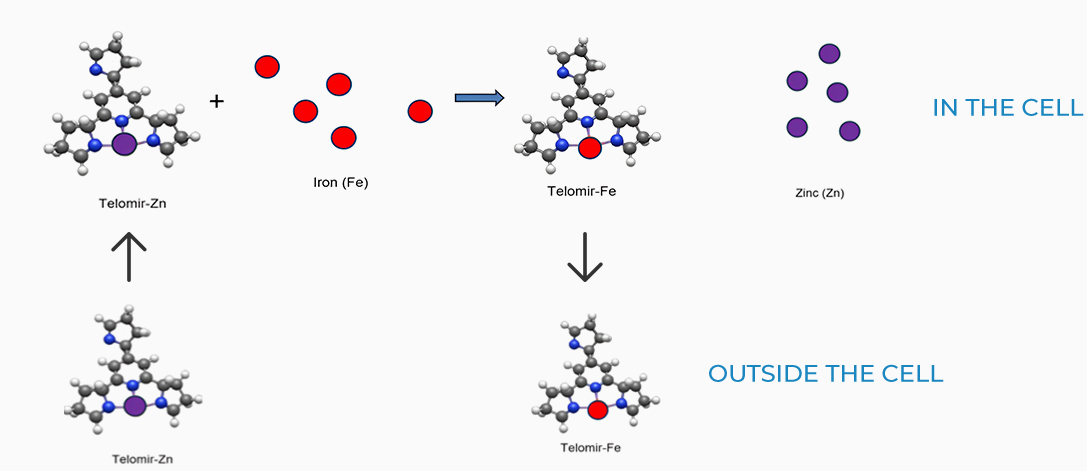
Exchange mechanisms
Due to the lower affinity of Telomir-1 to Zinc, compared with Iron, Telomir-Zn will exchange the free Iron levels in the cells with beneficial Zinc and will chelate the free iron and take it outside the cell.
telomere and telomer length
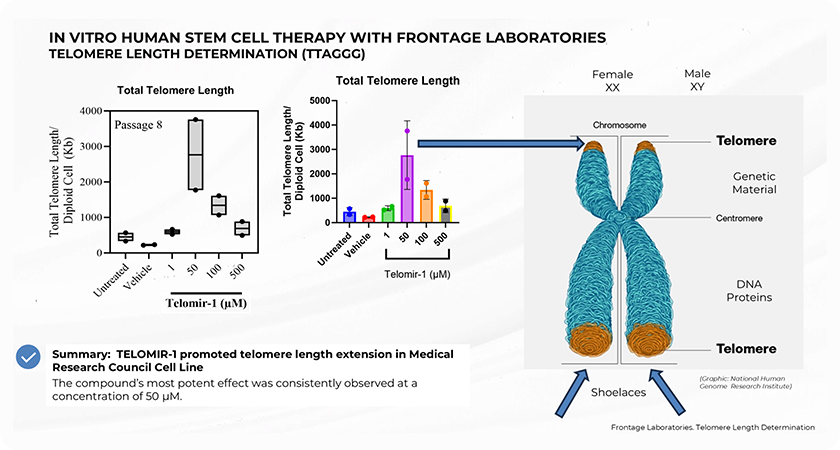
Study Summary and Methodology
The preclinical study, conducted in collaboration with Nagi Bioscience SA, utilized a sophisticated in vivo microfluidic-based assay to assess the effects of Telomir-1 on the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, a well-established model for aging studies. The microfluidic platform allowed precise, automated tracking of lifespan, healthspan, and age-related mobility decline in real-time, enabling the research team to accurately measure the effects of Telomir-1 on these critical metrics.
Two forms of Telomir-1 were administered in two concentrations, allowing the study to examine dose-dependent responses in treated subjects. The study found that Telomir-1 significantly enhanced lifespan and healthspan parameters in aged microorganism populations.
Key Findings Included:

Increased Lifespan
Telomir-1 was associated with a statistically significant increase in lifespan among treated populations. This further supports Telomir-1’s role in promoting longevity.
Enhanced Mobility in Older Organisms
Subjects treated with Telomir-1 showed improved motility, particularly in later stages of life, compared to untreated controls. This enhanced movement in advanced age suggests a slowing of the aging process, as mobility is a key indicator of biological health.

Reduced Biological Aging
The study demonstrated a measurable reversal of biological age markers in subjects treated with Telomir-1. This significant finding points to Telomir-1’s potential to slow down, and in certain aspects, reverse biological aging, making it a promising candidate for longevity treatments.
Effect on median lifespan
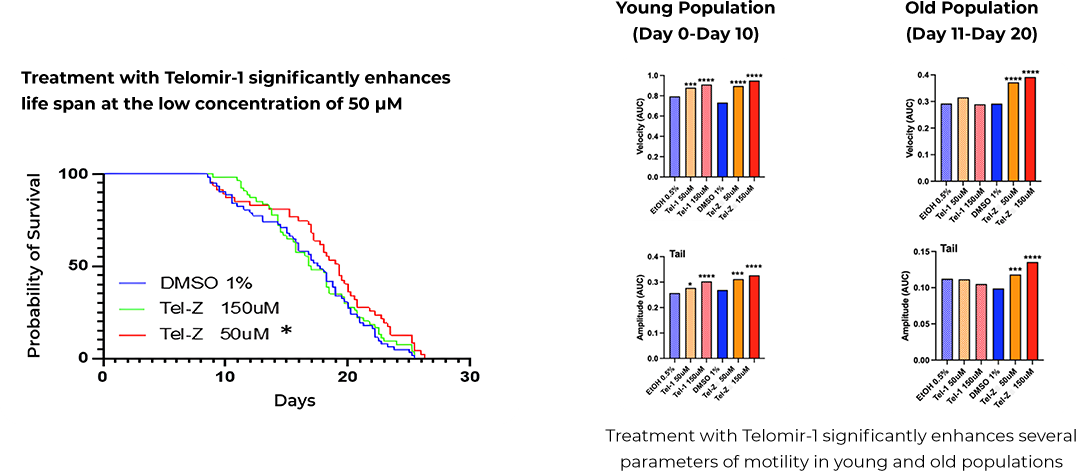
Study in Progeria – Summary and Methodology
The preclinical study with Nagi Bioscience SA used C. elegans with a wrn-1 gene mutation, the human equivalent of which is linked to Werner Syndrome (Progeria), showing reduced life expectancy compared to wild-type nematodes.
Key Findings Included:

Increased Lifespan
The study demonstrates significant age-reversal effects in wrn-1 mutated nematodes treated with Telomir-1. It was demonstrated that this treatment was capable to effectively bring the longevity level back to levels which are not significantly different from normal animals
Enhanced Mobility in Older Organisms
These effects include an extended healthy lifespan and normalization of several other physiological parameters such as movement velocity and tail amplitude.